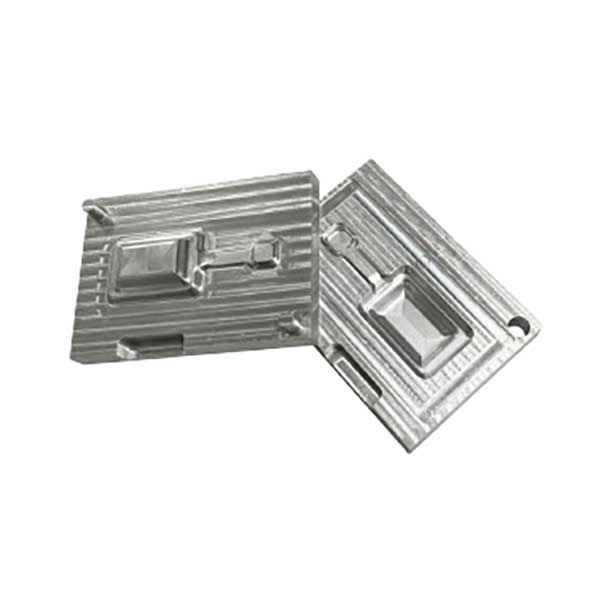
Aluminum Injection Mold Tooling Service
Custom Aluminum Injection Mold Tooling Service
Order custom aluminum injection mold tooling with fast turnaround times and cost-effective pricing. We offer a variety of aluminum materials and finishes suitable for both prototype development and full production runs.
- ISO 9001 & ISO 13485 Certified Factory
- Advanced Equipment & Competitive Pricing
- Over 10 Years of Experience in Aluminum Injection Mold Tooling
- Tight Tolerances of 0.001 mm
- Wide Range of Aluminum Material Options Available
- 24/7 Engineering Support

Our Aluminum Injection Mold Tooling Capabilities
Aluminum is a versatile and durable material that is widely used in injection mold tooling. It offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it a top choice for mold manufacturing. With its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and superior thermal conductivity, aluminum is commonly used across industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, electronics, consumer goods, and packaging. After injection molding, aluminum exhibits minimal risk of deformation or surface defects, and it is easy to finish, color, and polish, making it ideal for producing high-quality, precise molds.
Price | $ |
Lead Time | <7 days |
Wall Thickness | 0.75 mm |
Tolerances | ±0.125mm(±0.005″) |
Max Part Size | 200x80x100cm(78.74”x31.5”x39.37”) |
Available Aluminum at NOBLE | Aluminum6061, 2024, 5052, 5083, 6061-T6, 6063, 6082, 7075, 7075-T6.ADC12(A380) |

Characteristics of Injection Mold Tooling Materials
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used materials for injection mold tooling due to its excellent properties. Below are some key characteristics of aluminum that make it an ideal choice for mold manufacturing:
Features | Info |
Subtypes | 6061-T6, 7075-T6, 7050, 2024, 5052, 6063, etc |
Process | Injection mold tooling, CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication |
Tolerance | With drawing: as low as +/- 0.005 mm No drawing: ISO 2768 medium |
Applications | Light & economic, used from prototyping to production |
Finishing Options | Alodine, Anodizing Types 2, 3, 3 + PTFE, ENP, Media Blasting, Nickel Plating, Powder Coating, Tumble Polishing. |
Pros and Cons of Aluminum for Injection Mold Tooling
Aluminum is a popular material for injection mold tooling due to its light weight, excellent machinability, and versatility. It is favored in industries requiring efficient, high-performance molds, especially for short to medium production runs. However, it also has some limitations, such as lower strength compared to steel, wear susceptibility, and potential challenges related to thermal expansion and surface durability. Selecting the proper aluminum alloy and mold design can help mitigate these challenges.
Lightweight
Aluminum alloys are much lighter than steel, making them ideal for injection molds that need to be moved quickly or have a reduced weight to support the production of lighter plastic parts. This feature is particularly beneficial in industries like consumer electronics and automotive.
Excellent Machinability
Aluminum is easier to machine than many other metals, allowing for faster mold production and high-precision mold cavities. This results in lower tooling costs and shorter lead times for mold manufacturers.
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum’s natural oxide layer provides excellent protection against corrosion, making it a good choice for molds exposed to humid environments or certain types of plastics that may be corrosive.
Good Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 or 7075, provide a good balance of strength and weight, making them suitable for injection molds that require structural integrity without the excessive weight of steel molds.
Versatility
Aluminum alloys are available in a variety of grades and compositions, offering properties such as better weldability, improved surface finish, and resistance to corrosion. This versatility allows for customized mold designs that can meet specific product requirements.
Recyclability
Aluminum is 100% recyclable without degradation of its properties, making it an environmentally friendly option for injection molds and contributing to cost savings over time.
Thermal Conductivity
Aluminum has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps improve cycle times in injection molding by promoting efficient heat transfer. This can enhance production efficiency and part quality, especially for molded parts that require quick cooling.
Cost-Effectiveness
Aluminum molds, especially for low-to-medium volume production, are often more cost-effective than steel molds. They offer a good balance of performance and affordability for applications where high production rates are not critical.

Lower Strength Compared to Steel
While aluminum molds are sufficient for many applications, they are not as strong as steel molds, which can limit their use for high-pressure molding or long production runs. In these cases, steel may be a better choice due to its higher wear resistance.
Softness and Wear Sensitivity
Aluminum is softer than steel, which makes it more prone to wear and surface damage, especially when molding abrasive plastics or running molds with high cycle counts. This may result in the need for more frequent maintenance or repairs.
Tool Wear
Although aluminum is easier to machine, it can still cause tool wear during the initial mold creation, especially when dealing with high-strength aluminum alloys or when machining intricate mold features at high speeds.
Thermal Expansion
Aluminum’s high coefficient of thermal expansion can lead to dimensional changes during the injection molding process, particularly when rapid temperature fluctuations occur. This can affect part tolerances and the mold’s overall precision.
Relatively Higher Cost for High-Grade Alloys
While aluminum is generally less expensive than steel, high-performance aluminum alloys (such as 7075) used in molds for certain plastics or high-precision applications can still be costly.
Potential for Surface Damage
Aluminum molds may experience surface degradation due to abrasive or chemically reactive plastics, which can impact mold longevity. Protective coatings or anodizing treatments can be used to improve surface hardness and corrosion resistance, but these treatments add additional cost and complexity.

Types of Aluminum Injection Mold Tooling Materials
NONLE has worked with various aluminum subtypes for injection mold tooling, offering a wide selection of materials tailored to different mold requirements:

Aluminum 6061-T6
6061 aluminum is a versatile alloy commonly used in injection mold tooling due to its excellent machinability, corrosion resistance, and weldability. It is ideal for creating molds for applications in aerospace, automotive, marine, construction, and consumer goods, offering a good balance of strength and weight.
Yield Strength(MPa): 276
Elongation at Break(%): 17
Hardness(Brinell): 95
Density(G/m³): 2.7
Maximum Temp: 1080° F

Aluminum 7075-T6
7075 aluminum is known for its superior strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice for high-performance mold tooling. Its resistance to stress corrosion and high strength makes it ideal for injection molds used in aerospace, military, and automotive applications, where durability and precision are critical.
Yield Strength(MPa): 503
Elongation at Break(%): 11
Hardness(Brinell): 150
Density(G/m³): 2.8
Maximum Temp: 380° F

Aluminum 5052
5052 aluminum is widely used for injection mold tooling due to its excellent corrosion resistance and formability. It is ideal for marine, automotive, and chemical industries. Its great weldability and ability to withstand harsh environments make it a good choice for producing molds that require high performance under demanding conditions.
Yield Strength(MPa): 193
Elongation at Break(%): 12
Hardness(Brinell): 60
Density(G/m³): 2.68
Maximum Temp: 300° F

Aluminum 6063
6063 aluminum is often used in injection mold tooling for architectural applications, such as window and door frames, as well as structural components. Known for its excellent surface finish, ease of machining, and good corrosion resistance, it is ideal for molds used in consumer goods and building materials.
Yield Strength(MPa): 214
Elongation at Break(%): 12
Hardness(Brinell): 73
Density(G/m³): 2.7
Maximum Temp: 212° F

Aluminum 6061
6061 aluminum is a widely used alloy in the manufacturing of injection molds due to its good strength, corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability. It is ideal for producing molds for automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications, ensuring high-quality results in mass production.
Yield Strength(MPa): 276
Elongation at Break(%): 17
Hardness(Brinell): 95
Density(G/m³): 2.7
Maximum Temp: 300° F

Aluminum 2024
Aluminum 2024 is a high-strength alloy that is commonly used for injection mold tooling in high-stress, precision applications. Known for its excellent fatigue resistance and ability to withstand extreme conditions, it is ideal for molds in industries such as aerospace, defense, and other high-performance sectors. Aluminum 2024 is highly suitable for complex mold cavities that require exceptional strength and durability.
Yield Strength(MPa): 325
Elongation at Break(%): 20
Hardness(Brinell): 120
Density(G/m³): 2.78
Maximum Temp: 935° F

Aluminum 5083
Aluminum 5083 is renowned for its superior corrosion resistance, especially in saltwater environments, making it an excellent choice for injection mold tooling used in marine, transportation, and industrial applications. Its high strength and resistance to wear make it ideal for producing durable and long-lasting molds for components exposed to harsh conditions.
Yield Strength(MPa): 275
Elongation at Break(%): 12
Hardness(Brinell): 75
Density(G/m³): 2.66
Maximum Temp: 775 °F

Aluminum 6082
Aluminum 6082 is widely used for molds in structural applications, including those in the construction and transportation sectors. Known for its excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability, it is a great choice for injection mold tooling that requires high-performance in demanding industrial environments.
Yield Strength(MPa): 260
Elongation at Break(%): 11
Hardness(Brinell): 95
Density(G/m³): 2.7
Maximum Temp: 330 °F

Aluminum 7075
Aluminum 7075 is a top choice for injection mold tooling in high-performance applications due to its outstanding strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to stress and fatigue. It is commonly used in aerospace, defense, and sports equipment manufacturing, where precise, durable molds are required to create lightweight, high-strength parts.
Yield Strength(MPa): 503
Elongation at Break(%): 11
Hardness(Brinell): 150
Density(G/m³): 2.81
Maximum Temp: 775 °F

Aluminum ADC12 (A380)
Aluminum ADC12 (A380) is a widely used alloy in the automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries. It offers excellent fluidity, castability, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for producing injection molds for components. This alloy is perfect for molds used in automotive parts, engine components, and transmission housings, where precision and material durability are critical.
Yield Strength(MPa): 160
Elongation at Break(%): 3.5
Hardness(Brinell): 80
Density(G/m³): 2.74
Maximum Temp: 572 °F
Surface Finishing Options for Injection Mold Tooling
Our superior surface finishes can make your custom injection molds stand out even more. We offer a diverse range of finishing solutions to enhance the surface quality of your molds. These coatings also improve the mechanical strength and durability of your molds.

Glossy
A grade finishes are made using a diamond buffing process and yield shiny and glossy surfaces on injection molded parts.

Semi-glossy
B grade finishes use grit sandpaper to produce parts with a slightly rougher finish than grade A parts. Custom molded plastic parts that undergo B grade finishing have a matte surface texture.

Matte
C grade finishes use grit sanding stones to produce a rough, uneven surface. Injection plastic parts that undergo C grade finishing have a matte surface texture.

Textured
D grade finishes use grit and dry glass beads or oxide to produce a very rough textured finish. Depending on the type of material used, products can have a satin or dull finish.
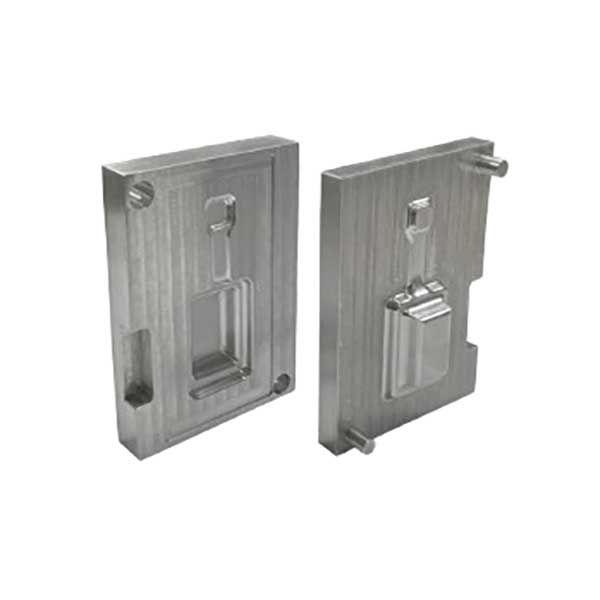
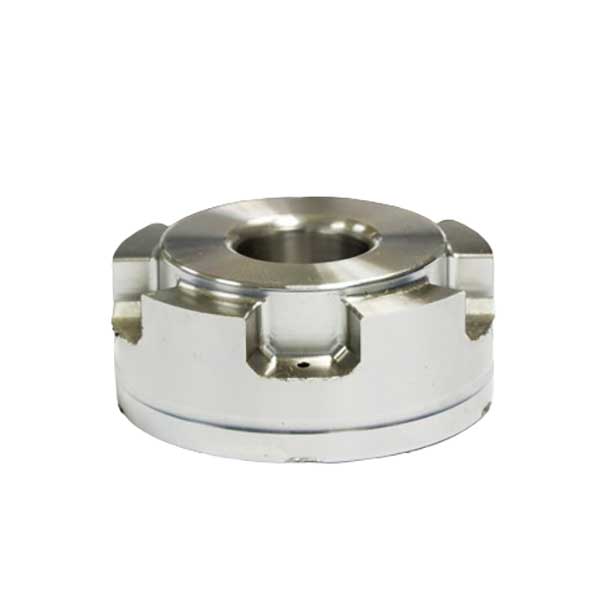
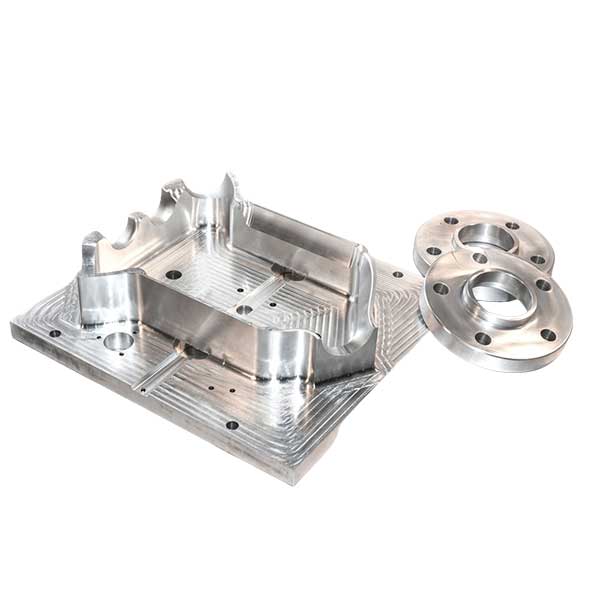
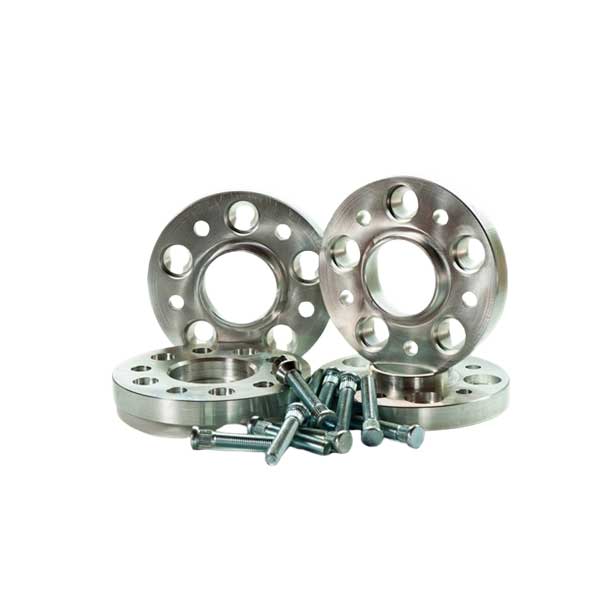
Custom Aluminum Mold Tooling Parts Display
Check out our over ten years of custom aluminum mold tooling, including precision aluminum prototypes and parts from our valued customers.
Applications of Aluminum Injection Mold Tooling
Aluminum injection mold tooling is widely utilized across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical devices, and robotics, for producing lightweight, high-precision components such as aircraft parts, enclosures, surgical instruments, and robotic components.

Automotive Parts
Aluminum injection mold tooling is heavily used in the automotive industry to produce lightweight, high-performance components. By utilizing aluminum, manufacturers can reduce the overall weight of vehicles, leading to improved fuel efficiency, better handling, and enhanced vehicle performance.

Aerospace Parts
In the aerospace sector, aluminum injection mold tooling is employed to manufacture lightweight and strong components, such as fittings, brackets, housings, and interior parts, which are critical for reducing the overall weight of aircraft. Aluminum's strength-to-weight ratio makes it perfect for aerospace applications where both durability and lightness are essential to ensure safe and efficient flight.

Medical Devices
Aluminum injection mold tooling plays a crucial role in the medical industry by producing lightweight, high-precision components like surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment housings, and implantable devices. Aluminum's biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and ability to achieve tight tolerances make it an excellent choice for medical device manufacturers requiring high-quality, reliable components.

Robotics Parts
In the robotics industry, aluminum injection mold tooling is essential for producing precision components such as robotic frames, joints, gears, and connectors. Aluminum's lightweight and strong properties help create efficient and reliable robotic systems that can handle complex movements and dissipate heat effectively, enabling robots to perform specific functions with higher precision and longer operational lifespans.

Industrial Equipment
Aluminum injection mold tooling is widely used in the production of lightweight and durable components for industrial equipment. It allows for the creation of complex, high-precision parts that are vital to machinery performance and operational efficiency. Aluminum components contribute to equipment longevity and performance, offering flexibility in design and customization for various industrial applications.

New Energy
In the new energy sector, aluminum injection mold tooling supports the production of lightweight, precise components essential for the development of renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and battery housings.
If you are looking for a rapid prototyping manufacturer or a CNC machine shop to fabricate small, medium-volume, or mass-production products, NOBLE is an ideal choice.Our well-trained and experienced staff manufactures parts in line with drawings on modern CNC machines, with the highest accuracy and processing quality in all sizes.In addition, we provide professional design considerations for your CNC machining projects.
Want to get the most professional and fastest service for your CNC machining project? Upload your CAD files now and obtain a quote!